All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
Inherited annuities come with a death advantage, which can provide monetary protection for your enjoyed ones in the event of your fatality. If you are the recipient of an annuity, there are a couple of guidelines you will need to comply with to inherit the account.
Third, you will certainly need to provide the insurance provider with various other needed paperwork, such as a copy of the will or count on. 4th, relying on the kind of acquired annuity and your individual tax obligation scenario, you might need to pay taxes. When you inherit an annuity, you should pick a payout choice.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/grat.asp-final-687dbf83454840fd857a94e53eb6172c.png)
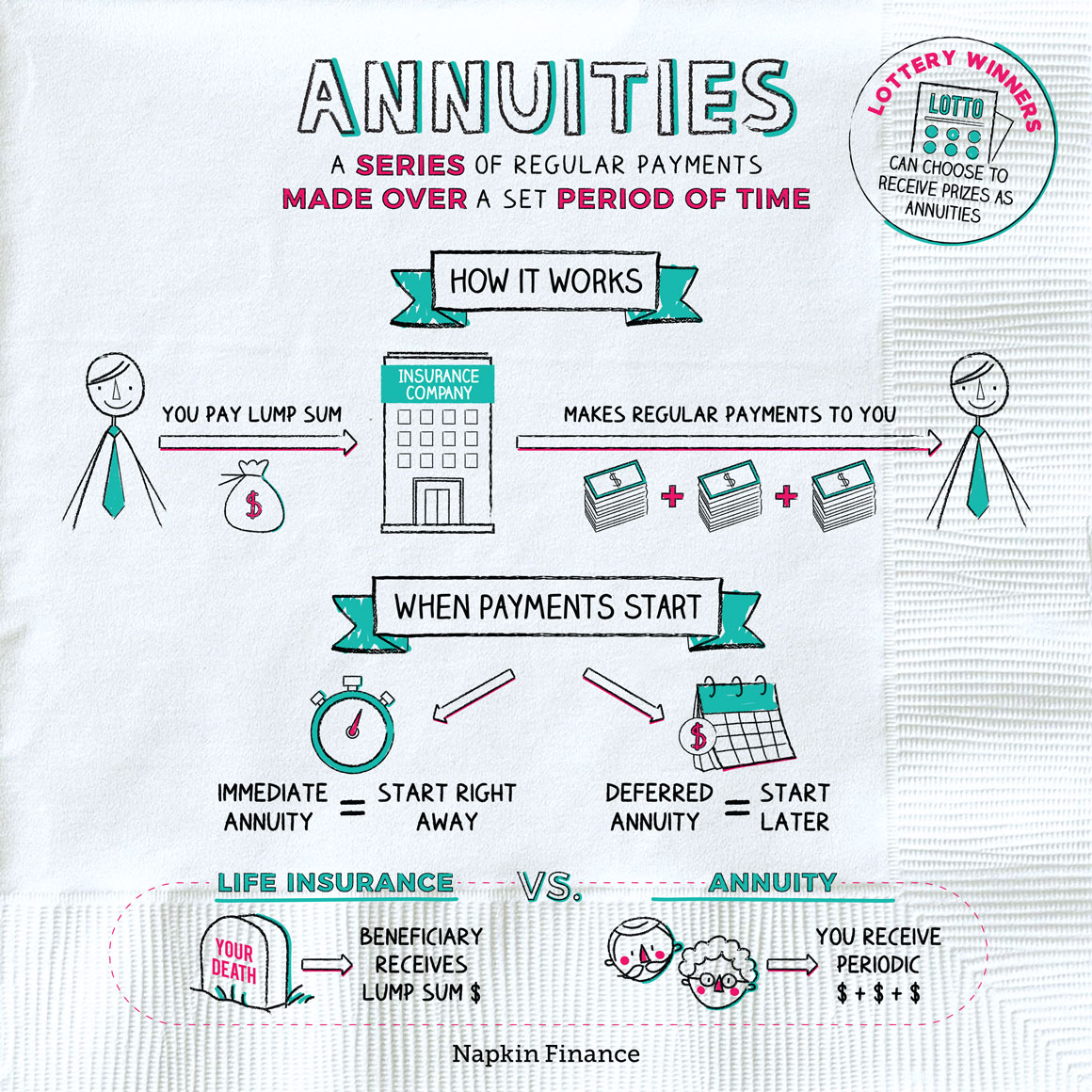
With an immediate payment choice, you will certainly start receiving payments as soon as possible. The payments will certainly be smaller than they would certainly be with a delayed option since they will be based on the present worth of the annuity. With a deferred payout alternative, you will certainly not begin getting settlements later on.
When you inherit an annuity, the taxes of the account will certainly depend on the kind of annuity and the payout option you pick. If you acquire a traditional annuity, the repayments you obtain will certainly be strained as ordinary earnings. If you inherit a Roth annuity, the settlements you receive will certainly not be exhausted.
How are Flexible Premium Annuities taxed when inherited
If you select a deferred payment option, you will certainly not be strained on the development of the annuity till you begin taking withdrawals. Talking with a tax expert before inheriting an annuity is crucial to ensure you recognize the tax ramifications. An acquired annuity can be a terrific means to provide economic safety for your liked ones.
You will certainly likewise require to adhere to the guidelines for inheriting an annuity and choose the right payment choice to match your demands. Be certain to speak with a tax obligation advisor to ensure you recognize the tax obligation implications of acquiring an annuity - Lifetime annuities. An acquired annuity is an annuity that is given to a recipient upon the fatality of the annuitant
To acquire an annuity, you will require to supply the insurance policy firm with a copy of the fatality certification for the annuitant and fill in a recipient kind. You might need to pay taxes depending upon the kind of inherited annuity and your individual tax obligation circumstance. There are two primary kinds of inherited annuities: standard and Roth.

The taxation of an acquired annuity will depend upon its type and the payout option you pick. If you inherit a traditional annuity, the payments you receive will be taxed as regular earnings. Nevertheless, if you inherit a Roth annuity, the settlements you get will certainly not be exhausted - Annuity payouts. If you choose a prompt payment choice, you will be tired on the annuity's growth up to the date of inheritance.
Tax on Lifetime Annuities death benefits for beneficiaries
How an inherited annuity is exhausted depends upon a variety of factors, however one trick is whether the money that's coming out of the annuity has been tired prior to (unless it remains in a Roth account). If the cash distributed from an annuity has not been strained previously, it will be subject to tax.
In addition to owing income tax obligations, you may be hit with the internet investment revenue tax of 3.8 percent on distributions of revenues, if you surpass the yearly thresholds for that tax. Acquired annuities inside an IRA likewise have special circulation rules and enforce various other needs on successors, so it is necessary to recognize those regulations if you do inherit an annuity in an IRA. A professional annuity is one where the proprietor paid no tax obligation on contributions, and it might be kept in a tax-advantaged account such as typical 401(k), traditional 403(b) or conventional individual retirement account. Each of these accounts is funded with pre-tax money, indicating that taxes have actually not been paid on it. Since these accounts are pre-tax accounts and revenue tax obligation has actually not been paid on any one of the cash neither payments neither incomes distributions will go through ordinary income tax obligation.
A nonqualified annuity is one that's been acquired with after-tax cash, and circulations of any contribution are exempt to income tax due to the fact that tax obligation has currently been paid on contributions. Nonqualified annuities contain two major kinds, with the tax therapy relying on the type: This sort of annuity is bought with after-tax cash money in a regular account.

This type of annuity is bought in a Roth 401(k), Roth 403(b) or Roth individual retirement account, which are all after-tax pension. Any kind of regular distribution from these accounts is without tax on both contributed cash and profits. At the end of the year the annuity company will certainly file a Type 1099-R that reveals specifically just how much, if any, of that tax obligation year's distribution is taxed.
Beyond income tax obligations, a beneficiary might also require to compute estate and estate tax. Whether an annuity is subject to earnings tax obligations is a completely separate matter from whether the estate owes estate tax on its value or whether the successor owes inheritance tax on an annuity. Inheritance tax is a tax obligation assessed on the estate itself.
The rates are dynamic and range from 18 percent to 40 percent. Private states may also impose an inheritance tax on money distributed from an estate. On the other hand, estate tax are tax obligations on a person who receives an inheritance. They're not evaluated on the estate itself however on the beneficiary when the possessions are obtained.
Tax treatment of inherited Annuity Income Stream
federal government does not examine estate tax, though six states do. Rates variety as high as 18 percent, though whether the inheritance is taxable depends on its size and your relationship to the giver. Those inheriting large annuities must pay focus to whether they're subject to estate taxes and inheritance tax obligations, beyond simply the basic revenue taxes.
Heirs ought to focus on prospective inheritance and estate tax obligations, too.
It's an agreement where the annuitant pays a swelling amount or a collection of costs in exchange for a guaranteed income stream in the future. What happens to an annuity after the proprietor passes away pivots on the particular information described in the agreement.
Various other annuities use a death advantage. This attribute enables the proprietor to assign a beneficiary, like a partner or child, to obtain the continuing to be funds. The payment can take the type of either the whole remaining equilibrium in the annuity or a guaranteed minimum quantity, normally whichever is greater.

It will clearly determine the recipient and possibly outline the readily available payout options for the death benefit. An annuity's death benefit assures a payment to a marked beneficiary after the proprietor passes away.
Table of Contents
Latest Posts
Decoding How Investment Plans Work A Closer Look at How Retirement Planning Works Breaking Down the Basics of Investment Plans Pros and Cons of Various Financial Options Why Fixed Annuity Or Variable
Decoding How Investment Plans Work A Comprehensive Guide to Investment Choices Breaking Down the Basics of Investment Plans Features of Variable Annuity Vs Fixed Indexed Annuity Why Fixed Vs Variable
Breaking Down Your Investment Choices A Comprehensive Guide to Retirement Income Fixed Vs Variable Annuity Breaking Down the Basics of Fixed Income Annuity Vs Variable Growth Annuity Pros and Cons of
More
Latest Posts